What is Rust Inhibitor ?
Anti-corrosion refers to the protection of metal surfaces from corroding in aggressive (corroding) environments. When the metal material put into the corrosive environment, itself would have chemical reaction with the air. It brings corrosive phenomenon on its surface. For example, after putting the iron into the corrosive atmosphere for a long time, the iron starts rusting due to oxygen interacting with water on the iron’s surface.
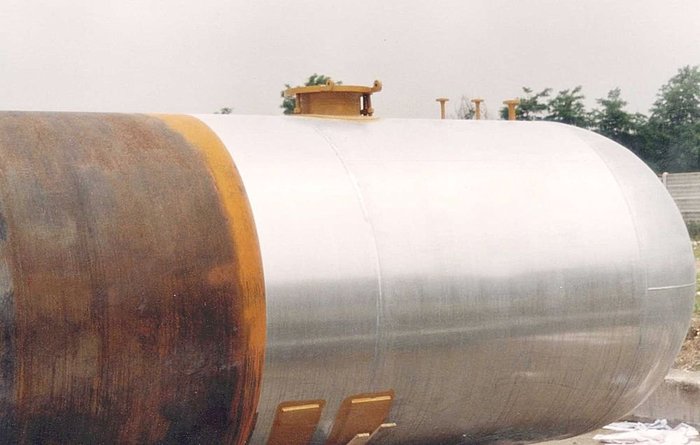

Therefore, when normal electronic equipments which aren’t doing any preventive measurement, they may become rusted inside and outside of the metal housings for long time exposure. In order to prevent the corrosion, there are some ways for electronic equipments especially for marine application. For those electronic equipments where installed in salty and misty cabins are especially needed anti-corrosion measurements.
A corrosion inhibitor is a chemical compound that, when added to a liquid or gas, decreases the corrosion rate of a material, typically a metal or an alloy. The effectiveness of a corrosion inhibitor depends on fluid composition, quantity of water, and flow regime.
A common mechanism for inhibiting corrosion involves formation of a coating, often a passivation layer, which prevents access of the corrosive substance to the metal. Permanent treatments such as chrome-plating are not generally considered inhibitors, however. Instead corrosion inhibitors are additives to the fluids that surround the metal or related object.
Protecting Metals from Corrosion
Ideally, a material which is inherently resistant to its service environment, meets with the mechanical, formability and economic requirements would be the first choice for selection. Unfortunately, this is not often the case. Many materials will need a method of corrosion control and there are three main approaches :
- Modification of the environment to which the material is exposed
- Electrical methods of control
- Use of protective coatings
Thermal Spray Coatings for Corrosion Protection
Thermal spray coatings are widely used in preventing corrosion of many materials, with very often, additional benefits of properties such as wear resistance etc. due to the very wide selection of coatings that can be sprayed. Broadly, thermal spray coatings fall into three main groups :
- Anodic Coatings
- Cathodic Coatings
- Neutral Coatings
Anodic Coatings
Anodic coatings for the protection of iron and steel substrates are almost entirely limited to zinc and aluminium coatings or their alloys. Where coatings anodic to the substrate are applied, the corrosion protection is referred to as cathodic protection or sacrificial protection. The substrate is made to be the cathode and the coating the sacrificial corroding anode. The mechanisms of corrosion protection inferred by these coatings fall into two classes :
- Cathodic or sacrificial protection
- A barrier to the environment
Cathodic Coatings
Cathodic coatings are those which comprise a coating metal which is cathodic with respect to the substrate. A stainless steel or nickel alloy coating would be cathodic to a steel base. Cathodic coatings can provide excellent corrosion protection.
There is a very wide choice particularly for steel base materials ranging from stainless steel to more exotic materials like tantalum to cater for the more extreme corrosive environments. However, an outstanding limitation of such coatings is that they must provide a complete barrier to the substrate from the environment. If the substrate is exposed to the corrosive environment, the substrate will become the anode and corrosion will be dramatically accelerated resulting in spalling of the coating.
Neutral Coatings
Neutral materials such as alumina or chromium oxide ceramics provide excellent corrosion resistance to most corrosive environments by exclusion of the environment from the substrate. Generally a neutral material will not accelerate the corrosion of the substrate even if the coating is somewhat permeable (An exception to this is with stainless steel type materials where the exclusion of oxygen can cause crevice corrosion, nickel chromium bond coats are required to stop this), although any corrosion of the substrate interface with the coating should be avoided to prevent coating separation. Again sealing of the coatings is recommended. The densest and thickest plasma sprayed coatings are recommended.
You might also like
| Nano Coatings What is Nano Coating ? The nano coatings,... | Galvanized Steel - a Definition What is Galvanized Steel ? Sheet, strip,... | What is Stainless Steel? Stainless Steel - A Definition Stainless... | Corrosion What is Corrosion ? Corrosion is the disintegration... |



 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers
 Aluminum
Aluminum
 Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions
 Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze
 Nickel
Nickel
 Magnets
Magnets
 Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
 Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing
 Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers
 Titanium
Titanium
 Tungsten
Tungsten
 Wire Rope
Wire Rope