Indium tin oxide (ITO, or tin-doped indium oxide) is a solid solution of indium(III) oxide (In2O3) and tin(IV) oxide (SnO2), typically 90% In2O3, 10% SnO2 by weight.
 Indium Tin Oxide
Indium Tin Oxide
As with all transparent conducting films, a compromise must be made between conductivity and transparency, since increasing the thickness and increasing the concentration of charge carriers will increase the material’s conductivity, but decrease its transparency.
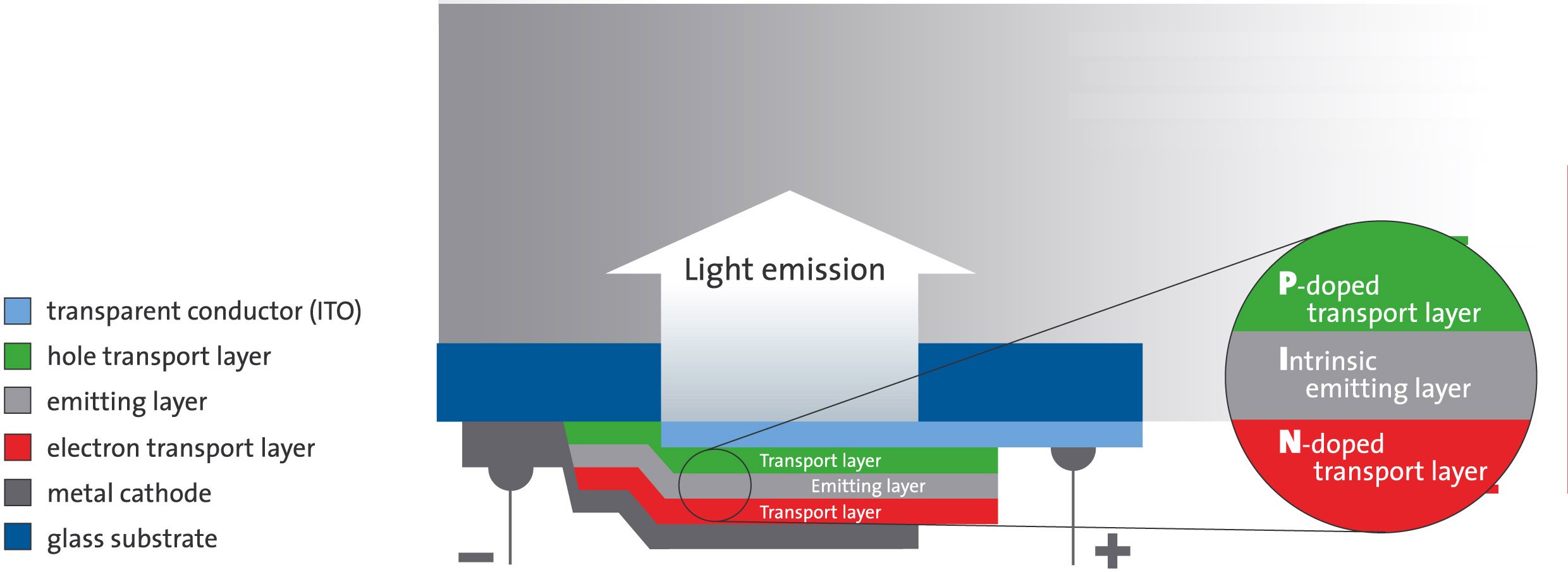 In an organic light-emitting diode (OLED), holes and electrons are injected into a stack of organic layers, which are usually sandwiched between a transparent indium tin oxide (ITO) electrode and a metal electrode. Electrons and holes recombine in the emission zone of the device, which contains organic emitter dyes. Here, excitons are formed by the combining charge carriers, which eventually decay and emit as visible light.
In an organic light-emitting diode (OLED), holes and electrons are injected into a stack of organic layers, which are usually sandwiched between a transparent indium tin oxide (ITO) electrode and a metal electrode. Electrons and holes recombine in the emission zone of the device, which contains organic emitter dyes. Here, excitons are formed by the combining charge carriers, which eventually decay and emit as visible light.
Thin films of indium tin oxide are most commonly deposited on surfaces by electron beam evaporation, physical vapor deposition, or a range of sputter deposition techniques.
You might also like
| Semiconductor Materials A semiconductor is a substance,... | The Bayer and Hall-Heroult Process Aluminum manufacture is accomplished... | Corrosion Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered... | What is Diamond? Diamond is less stable than graphite,... |


 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers
 Aluminum
Aluminum
 Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions
 Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze
 Nickel
Nickel
 Magnets
Magnets
 Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
 Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing
 Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers
 Titanium
Titanium
 Tungsten
Tungsten
 Wire Rope
Wire Rope